Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
Learn the latest and greatest strategies, tools, best practices in the world of generative engine optimization. This guide covers:
- Most effective GEO strategies based on data and field observations
- Tips for learning GEO quickly (including experts worth following)
- How to track traffic and visibility from from LLMs
- Several more resources for marketers learning GEO

Key Takeaways
- Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) represents the next evolution of classic SEO, shifting emphasis toward earning brand mentions and citations directly inside AI-generated responses from large language models such as ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, Claude, DeepSeek, and Grok, rather than focusing solely on rankings within link-driven search engines.
- GEO adds on to core SEO fundamentals instead of replacing them (site speed, mobile optimization, backlinks), while layering in new strategies like targeting conversational prompts, structuring easily digestible content formats (question-based headings, bullet lists, tables), strengthening E-E-A-T signals, deploying schema markup, and repurposing content across multiple platforms (e.g., Reddit, YouTube, and X).
- Popular GEO tactics include whitelisting AI bots for crawling, implementing llms.txt files (shown to drive significant traffic increases), digital PR for authority, marketing on UGC sites, and platform-specific adjustments (e.g., PDFs for Claude, X posts for Grok).
- Primary GEO metrics shift from traditional rankings and organic traffic to prompt tracking, AI visibility (mentions/citations), share of voice in LLMs, and referral traffic from AI platforms.
- A range of GEO tools exist for monitoring visibility across LLMs, from affordable options like Cairrot (with WordPress integration and Grok support) and pay-per-report tools like Gumshoe, to enterprise solutions like Evertune; tool choice depends on budget, needs (e.g., API access), and scale.
- In a hybrid SEO-GEO world, brands should emphasize cross-platform content distribution, content freshness, and a mix of manual and automated monitoring to build authority and capture emerging AI referral traffic.
- GEO and AEO (Answer Engine Optimization) are generally used interchangeabley, with AEO likely to become the standard due to broader adoption and less ambiguity. LLMO (LLM Optimization) and AIO (AI Optimization) are also commonly used when referring to GEO.
Table of Contents
What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
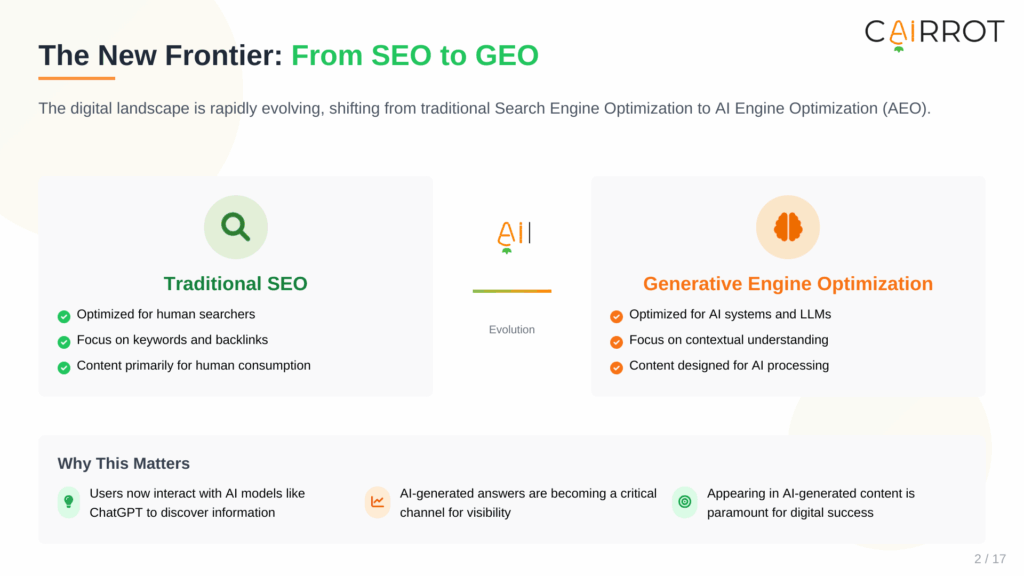
Within modern digital marketing, Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) represents the next stage of Search Engine Optimization (SEO), purpose-built for an environment dominated by Large Language Models (LLMs) and AI-powered discovery. Put simply, GEO is the intentional practice of optimizing websites, content assets, and brand signals so they can be surfaced, interpreted, and referenced by AI search experiences such as ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Perplexity, Claude, and Grok.
Where traditional SEO concentrates on positioning a webpage among a list of blue-link results, GEO shifts the objective toward embedding a brand’s facts, insights, and viewpoints directly inside AI-generated responses. As Conductor CEO Seth Besmertnik explains, AI has introduced a “parallel surface of visibility,” a largely unseen layer where brand awareness and trust are formed before a user ever reaches a clickable link (ALM Corp, 2025).
The objective, therefore, is no longer limited to ranking performance; it is about becoming the authoritative, reference-worthy source that AI search systems rely on to educate and guide their audiences.
GEO vs. SEO (Similar But Different)

Although GEO is built on top of traditional SEO principles, it introduces meaningful changes across three core dimensions: the metrics you measure, the channels driving visibility and traffic, and the optimization tactics you apply. Grasping these distinctions is essential for reshaping marketing strategies to succeed in an AI-first search environment.
At a fundamental level, GEO frameworks are designed to help answer high-impact questions such as:
Is my brand appearing when users submit relevant prompts or questions?
In what context are those brand mentions occurring?
Are competitors being surfaced more frequently than my brand?
Which specific pages, datasets, or content assets are being referenced by AI systems?
How does my overall visibility evolve over time across different AI models and platforms?
KPIs for GEO vs. SEO
How success is evaluated in search is undergoing a major shift. While classic SEO benchmarks still matter, GEO introduces a new class of KPIs centered on brand influence and visibility inside AI-generated responses.
- Traditional SEO metrics: Performance has historically been judged by leading indicators such as priority keyword rankings and average SERP position, along with lagging signals like organic traffic volume and conversions attributed to organic search.
- GEO metrics: The modern measurement framework emphasizes target prompts (the natural-language questions real users ask), AI visibility (how frequently a brand is mentioned or cited), share of AI voice, and downstream conversions driven by LLM referral traffic.
Based on extensive industry research, the most important GEO indicator is citation frequency—the number of times an AI system references your brand or domain as a trusted source in generated answers. This evolution reframes success around authority and influence, rather than clicks on their own.
Although basic LLM referral traffic can be monitored at no cost in Google Analytics 4 by filtering for sources such as chatgpt.com, more advanced GEO efforts require purpose-built tooling. Platforms like Cairrot provide deeper capabilities for measuring GEO-specific signals, including AI visibility, prompt-level performance, and brand mentions across multiple LLMs.
AI Traffic vs. Organic Traffic
For most companies, traditional organic traffic is overwhelmingly dominated by a single player: Google, which often accounts for over 90% of organic visits. The AI traffic landscape, however, is more dynamic.
Today, research from Conductor shows that ChatGPT accounts for a staggering 87.4% of all AI referral traffic, establishing it as the “Google of AI search” (ALM Corp, 2025). However, this market is far from settled. Competitors like Google Gemini, Anthropic’s Claude, and Perplexity are rapidly innovating and capturing niche audiences.
We are already seeing industry-specific preferences emerge. For example:
- If you are marketing a complex SaaS product, your ideal users may gravitate towards the sophisticated reasoning capabilities of Claude.
- If you are in media or an emerging industry, you might find that users on X’s Grok, which leverages real-time social data, convert at higher rates.
- Conductor’s research also found that Google Gemini has an unusually high market share (21%) in the Utilities sector, suggesting that different LLMs may develop vertical-specific strengths (ALM Corp, 2025).
This evolving ecosystem means that unlike the Google-centric world of SEO, a successful GEO strategy must be mindful of a multi-platform environment.
Differences in GEO Strategies vs Traditional SEO
GEO is not a replacement for SEO; it’s an expansion of it. The majority of your search strategy should still be grounded in SEO fundamentals, as traditional search continues to drive the lion’s share of traffic. However, digital marketers and SEO experts widely agree that specific GEO strategies must be layered on top of existing SEO checklists to ensure visibility in AI search.
As Pat Reinhart, VP at Conductor, advises, marketers should recognize that AI search “will grow over time and eventually ruin your long-term plans if you don’t account for it” (ALM Corp, 2025). The consensus at major SEO conferences is clear: you must integrate GEO tactics now to future-proof your brand. Key principles include:
- Build GEO tactics on top of a strong SEO foundation.
- Optimize content for conversational, question-based queries.
- Adhere to content structure best practices (e.g., clear headings, lists) that benefit both humans and AI.
We will explore these strategies in greater detail in the sections below.
Are GEO and SEO Different Roles?
Given that GEO tactics are typically implemented on top of existing SEO tasks, does this necessitate a new role? For most teams, the answer is no. GEO is an evolution of the SEO skillset.
However, that doesn’t mean roles can’t be specialized within a larger marketing team. It is becoming common for marketing agencies that specialize in AI search to have a division of labor. For instance, an AI Search Strategist might oversee the client account and define the high-level GEO strategy, while internal SEO Specialists focus on implementing the specific on-page, technical, and content optimizations required to achieve those goals.
Core Pillars of an Effective GEO Strategy

To succeed in AI search, digital marketers need a blended strategy that combines time-tested SEO foundations with emerging LLM-specific optimizations. The following strategies form the core pillars of an effective and scalable GEO program.
1. Build on SEO Fundamentals Without Abandoning Them
Above all else, resist the urge to abandon established SEO best practices. LLMs continue to depend on organic search results to collect information, so by optimizing for SEO you are taking crucial steps towards AI visibility. Many of the same authority and relevance signals traditional search engines have relied on for years. Website performance, mobile responsiveness, clean site structure, and a strong backlink profile remain essential requirements for both SEO and GEO effectiveness.
Research consistently shows that we now operate in a “hybrid, dual-channel environment,” where classic search and AI discovery coexist. Although AI-driven referrals are increasing, organic search still accounts for a significant share of total traffic, reaching as high as 42.4% in Health Care and 39.6% in Communication Services (ALM Corp, 2025). For this reason, GEO should be viewed as a progression of SEO, not a wholesale replacement.
Tactic: Review your highest-performing pages (the ones already earning trust from Google) and enhance them with AI-compatible elements such as conversational Q&A blocks and concise executive summaries. This approach amplifies proven assets instead of rebuilding content from scratch.
2. Align Content Topics With Conversational Prompts and Intent
One of the most significant content shifts driven by GEO is the move away from isolated keyword targeting toward fully formed, conversational questions. When users interact with AI assistants, they speak naturally, asking questions like, “What are the best noise-canceling headphones under $200?” rather than entering fragmented keyword phrases.
Your content strategy should mirror this behavior. Leverage resources such as AnswerThePublic, Google’s “People Also Ask” sections, and internal customer support conversations to uncover the real questions your audience is asking. This ensures your content directly matches user intent and increases its likelihood of being selected for LLM citations.
Tactic: Develop topic clusters anchored by a comprehensive pillar page. Surround that pillar with supporting articles that address specific long-tail questions. This interconnected structure signals depth, coverage, and subject mastery to AI systems (Insidea, 2025).
3. Update Your Onpage SEO Checklists for GEO
AI models don’t read content the way humans do, they extract information quickly by scanning structural and semantic signals within HTML. To improve interpretability and summarization, content must be formatted for speed and clarity:
- Headings (H1, H2, H3): Phrase headings as direct questions (e.g., “How Do You Implement Schema Markup?”).
- Lists: Use bullet points and numbered lists to break down information into digestible steps or points.
- Tables: Use tables for comparisons (e.g., product features, pricing tiers).
- Short Paragraphs: Avoid dense walls of text. Keep paragraphs to 2-4 sentences.
- Answer Capsules: Begin articles or key sections with a concise, 40-100 word summary that directly answers the main question before elaborating further (ALM Corp, 2025).
In addition, structured data plays a critical role. Implement schema markup to provide explicit context to AI systems. Particularly valuable schema types for GEO include FAQPage, HowTo, Article, and Organization. Structured data effectively acts as an instruction manual for answer engines, dramatically improving interpretation and inclusion rates.
Tactic: Add clearly marked FAQ or Q&A sections to your priority pages and implement FAQPage schema to align your content with the formats LLMs prefer. Use questions in your H2 and H3 headings and answer the question with direct, natural language in your first two sentences.
4. Emphasize E-E-A-T (Trigger Expertise Signals)
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) remains Google’s quality framework, and it has become even more important in the context of GEO. AI systems are explicitly designed to prioritize reliable, authoritative sources, especially in high-risk “Your Money or Your Life” (YMYL) categories such as health, finance, and legal topics.
You can strengthen E-E-A-T by:
Highlighting Author Credentials: Clearly display author bios with relevant qualifications and experience.
Referencing Trusted Sources: Link to reputable studies, government publications, and expert commentary.
Publishing Original Research: Share proprietary data, surveys, or analyses—original datasets are strongly favored by LLMs (ALM Corp, 2025).
Securing Expert Reviews: Where appropriate, have content reviewed or endorsed by qualified professionals.
Conductor’s research in the Health Care sector illustrates this clearly: AI systems overwhelmingly reference organizations like Mayo Clinic and Cleveland Clinic due to their reputation, scale, and extensive libraries of expert-reviewed content.
Tactic: Reinforce your brand as a trusted entity through consistent naming, entity optimization, and earning citations or links from respected industry authorities. On a dedicated company page, highlight organizations that have recognized you, awards received, milestones of the business, executives who work there, and other elements of your business that should be highighted.
5. Distribute Content Across Multiple Platforms (“Rented Land” Strategy)
LLM search and agent tools search through dozens of web results and summarize their findings when users ask them a question. The implication is that repetition is key for staying visible in LLM search. Don’t just post content showing why you are the best option for your target customer on your own website; reformat that content and make it available on several websites (preferably ones with search traffic), as well as UGC and social media platforms (Reddit, YouTube, X, Linkedin, Threads, etc. are all great choices for various LLMs.
Tactic: Take blog content from your website, rewrite it so that at least 25% of the words are different, make sure it links back to another article on your website, and publish it on 3rd party websites like Medium.com and Linked in Pulse, as well as on any friendly websites in your industry that are interested in content sharing.
6. Favor Engagement and Freshness Over Content Volume
In a GEO-driven environment, depth and quality outweigh sheer output. AI models prefer content that is comprehensive, current, and well-maintained. Regularly update cornerstone pieces with fresh statistics, new insights, and revised examples to preserve relevance and “freshness” signals (Rellify, 2025).
This strategy also requires thoughtful bot management. While retrieval bots (such as GPTBot or Google-Extended) should be allowed to crawl your site for visibility, you may choose to block training bots if protecting proprietary content is a concern.
Tactic: Display information in engaging formats. For example, when comparing multiple competitors or products in an article, just don’t write paragraphs, use bullet points, tables, and images to relay related information in multiple formats.
7. Add LLM Specific Adjustments to Your SEO Strategy
AI visibility platforms like Cairrot surface behavioral differences across individual LLMs, making it possible to tailor optimizations by model. Because these insights are still relatively unknown, applying them early can create a meaningful competitive advantage.
Examples of effective model-specific tactics include:
Republishing content as PDFs to improve discoverability in Claude
Maintaining consistent brand mentions on Reddit to increase visibility in Gemini
Configuring Bing Webmaster Tools to improve inclusion in both Microsoft Copilot and ChatGPT
As with earlier strategies, this also involves optimizing bot access for retrieval while selectively restricting training crawlers when necessary.
Tactic: Validate optimization impact directly inside AI tools by testing prompts and tracking citation presence, brand mentions, and contextual tone.
8. Stay Focused on KPIs
Ultimately, performance marketing success is measured by metrics tied to revenue and the leading indicators that predict future growth. Historically, SEO teams focused on keyword rankings and Google SERP positions.
For GEO-focused teams, priorities shift toward prompt tracking and visibility measurement across key LLMs (typically ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, Perplexity, and Grok) alongside monitoring AI-driven referral traffic trends.
Because there is no tool that shows “LLM rankings” for free the way Google Search Console or Bing Wembaster Tools do for LLMs like Gemini and Grok, dedicated tools like Cairrot are needed to effectively “rank track” within LLMs, while baseline AI referral traffic can still be reviewed for free inside Google Analytics by filtering traffic sources associated with AI platforms.
Tools like Cairrot are required to “rank track” your position in LLMs, but anybody can check their website’s AI traffic for free in Google Analytics ->
Specific Examples of High-Impact GEO Tactics

Beyond broad strategies, several specific tactics have proven effective for digital marketers looking to gain an edge in AI visibility. Here are some of the most impactful examples we see working today.
1. Optimize for AI/LLM Crawlers (AI Readiness)
Your content cannot be referenced if AI crawlers are unable to reach it. This requirement extends far beyond managing a basic robots.txt file. Server settings, CDN rules, and firewall configurations must explicitly permit access from major AI crawlers, including non-LLM bots such as Amazonbot and Applebot, which support a wide range of AI-powered product and platform features.
Common AI crawler user agents that should be whitelisted include GPTBot, ClaudeBot, and PerplexityBot. URL structure also plays an increasingly important role: clear parent-child relationships and a logical content hierarchy help AI systems establish topical relevance and contextual understanding more effectively than ever before.
GEO tools like Cairrot immediately show you your “AI Readiness,” a score designed to show you how technically optimized your pages are for AI/LLM visibility.
Example:
- Grab a list of AI-related crawlers from a free resource like Github
- Make sure these crawlers are set to “allow” in your website’s robots.txt file
2. Generate LLMS.TXT In Addition to Schema Markup
Although not yet an officially confirmed ranking signal, many GEO practitioners believe the llms.txt file will eventually play a role in AI search comparable to the role sitemap.xml plays in traditional SEO. This lightweight text file, placed in a site’s root directory, enables publishers to signal which content LLMs should prioritize or ignore, while also communicating licensing preferences.
Early adopters report measurable gains in AI visibility after deploying structured llms.txt files. For instance, a Concurate case study documented a 5× increase in AI-generated referral traffic after optimizing their file to direct LLMs toward high-intent pages.
While working with marketing agencies like EWR Digital, I have also personally noticed that llms.txt files leads to more crawls from LLM bots on the pages that you link from the llms.txt file. Tools such as Cairrot’s llms.txt generator simplify this process by creating optimized files and deploying them automatically on WordPress sites.
Example:
- A WordPress website owner adding optimized llms.txt to their homepage automatically by installing Cairrot’s AI Logger plugin.
3. Digital PR (Link Building and Brand Mentions)
While backlinks and brand mentions (Digital PR) have always been important ranking factors in SEO (called offpage SEO or link building), their importance is magnified in GEO. The correlation between a strong authority profile (built through high-quality backlinks and mentions on reputable sites) and visibility in LLM responses is remarkably strong. AI models use these external signals as a proxy for trust. As a result, digital PR and strategic link building are becoming dedicated, critical functions within marketing teams focused on Generative Engine Optimization.
Examples of Digital PR designed for GEO include:
- Regular press releases: Even small companies should consider a press release every 6 months to get mentioned in news outlets and send links to your website. Most B2B companies should consider quarterly press releases at a minimum.
- Optimize your directory profiles: Make sure your profiles on review websites are up to date and show positive reviews. Ideally choose 2-3 platforms to focus on for reviews. These platforms should have high organic traffic and be known within your industry. For example, SaaS tools should optimize profiles on a combination of G2, SourceForge, Capterra, and TrustRadius.
4. Content Consolidations with Upgrades (Large Websites Only)
Websites with extensive content libraries often suffer from thin content or internal competition across overlapping articles. One effective remedy is content consolidation, or merging multiple underperforming URLs into a single, authoritative resource or landing page published under a new URL.
This tactic frequently improves both traditional SEO performance and AI visibility. Consolidation strengthens topical authority, improves user experience, and activates a renewed freshness signal when the consolidated content is republished.
Examples of consolidating content for GEO:
- A services company consolidating 50 location pages into their top 3 markets. If you rely on location-specific pages but aren’t winning traffic to most of them, consider combining them into your top three markets. Make the remaining pages much better than what existed before (improve copy, add imagery, emphasize positive reviews, etc.) and that all removed URLs are redirected to your remaining pages.
- A B2B company consolidating no-traffic blogs into long-form guides: If a B2B company has invested heavily in short-form content but hasn’t seen a traffic pickup, a common tactic is to combine short blogs into one long guide and redirect all the original URLs to the new URL of the guide.
5. Market on UGC Platforms Like Reddit, Quora, and Stack Overflow
When users ask questions, LLMs aggregate insights from dozens of online sources. This makes repetition across credible platforms a powerful visibility lever. Simply publishing content on your own site is no longer sufficient; key narratives should be repackaged and distributed across platforms with established trust and search visibility.
User-generated content (UGC) platforms, especially Reddit, have become major sources for AI models. Following its licensing deal with Google, Reddit content has seen a massive surge in visibility in search results. ChatGPT and other LLMs also frequently cite Reddit discussions to provide authentic, real-world perspectives and troubleshooting advice that corporate websites often lack. The Conductor AEO/GEO Benchmarks Report found that Reddit was one of the top-cited domains in the Communication Services industry (ALM Corp, 2025). Having a strong, positive presence in relevant subreddits is no longer just a community management task, it’s a core GEO tactic.
Example: Regularly take blogs from your own website; reformat that content and make it available on several websites (preferably ones with search traffic), as well as UGC and social media platforms (Reddit, YouTube, X, Linkedin, Threads, etc. are all great choices for various LLMs.
6. Leverage YouTube As an AI Knowledge Source
Modern transcription technology has made video content far more valuable than many marketers (especially SEOs) realize. AI systems can accurately transcribe YouTube videos, converting spoken language into searchable, indexable text at scale. As a result, every video functions similarly to a long-form article in terms of informational density.
This impact is reflected in Conductor’s research, which identified youtube.com as the most-cited domain in the Communication Services industry (ALM Corp, 2025). Brands that fail to share expertise through video miss a major opportunity to influence how LLMs understand and describe them.
Example: Many companies already have a video library for customer resources on their own platform. Reuploading that content to YouTube would likely improve visibility in LLMs like Gemini.
7. Repurpose Content Across Platforms
Each LLM draws from a unique mix of data sources. Maximizing AI visibility requires intentionally publishing content on the platforms each model favors, effectively “building on rented land.”
For example:
- To appear more often in Grok, you should post engaging, authoritative content on X (formerly Twitter).
- To improve your chances of being cited by Google Gemini and other LLMs that rely on Google’s index, share valuable content on platforms that rank well in Google search, such as Reddit, YouTube, LinkedIn, and even Instagram and TikTok.
This strategy involves understanding where AI models source their information and ensuring your brand is a prominent and trusted voice across that ecosystem. The level of control you have over your brand’s narrative varies significantly across these platforms, from full control on your own website to no control over news and forums.
7 Leading GEO Tools for Tracking AI Visibility
Here’s a a quick-view table comparing the top tools on the market. We dive deeper into each one below. See the next section for our master table comparing all these software tools in detail.
| GEO Tool | Starting Price | Key Differentiators | API | Free Trial |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cairrot | $39.99/month |
|
Yes (free) | Yes (contact for details) |
| Profound | $99/month |
|
No | Demo available (no free trial) |
| Gumshoe AI | ~$30 per report |
|
Yes (Enterprise plan) | Yes (first 3 reports free) |
| AthenaHQ | $295/month |
|
No | No |
| Evertune | $3,000/month |
|
No | No |
| Scrunch AI | $250/month |
|
Yes | Yes |
| Semrush AI Visibility Toolkit | $99/month |
|
No | No (free demo report available) |
We review each tool in great detail in our LLM Tracker Comparison ->
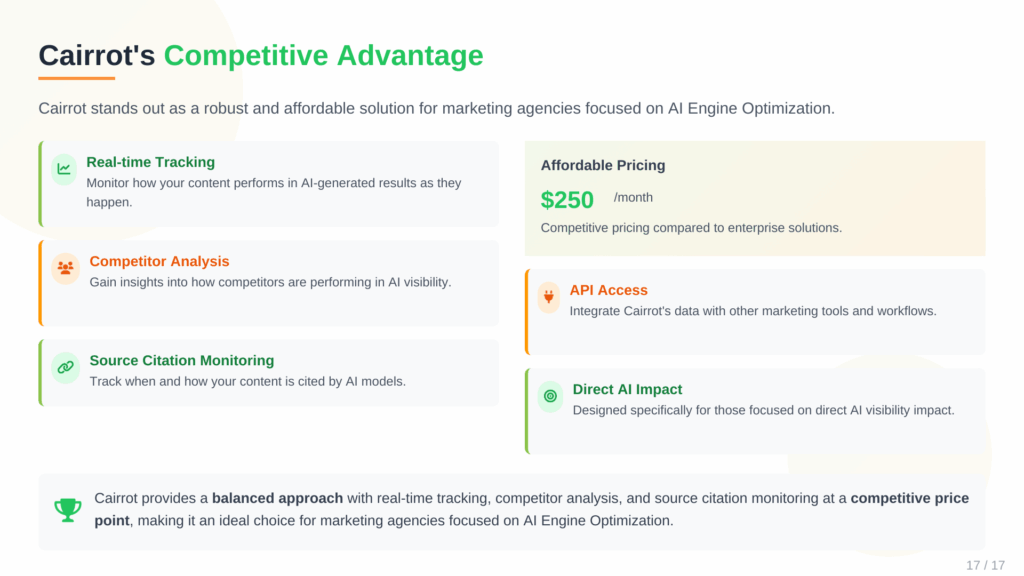
1. Cairrot (Affordable, Effective Option for Marketing Agencies and Companies Using WordPress)
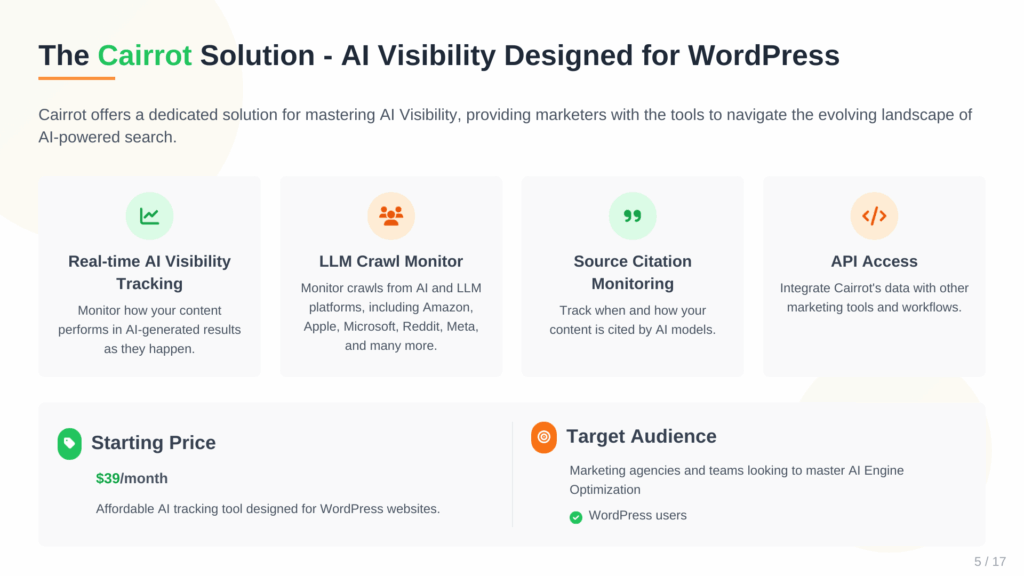
We built Cairrot because we needed powerful, flexible, and affordable way for our marketing agencies to manage GEO for their clients without getting locked into expensive, rigid contracts. We also believe most tools were not inspired, and the few that delivered what we wanted were obnoxiously expensive.
Cairrot was created on the idea that you should only pay for what you use, and that powerful features like an API shouldn’t be hidden behind an enterprise paywall.
- Key Features: LLM rank tracking (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, Claude, DeepSeek, and Grok), competitive analysis, citation monitoring, GEO recommendations.
- Pricing: Starts at $39.99/month for ChatGPT and Perplexity tracking. Its pricing model is per-client, so you only pay for active profiles.
- Free Trial: Yes, a full-featured free trial is offered.
- API: Yes, a robust API is included for free on all plans. This is, in my opinion, the best API for integrations in its price class.
- Integrations: The standout feature is its deep integration with WordPress. The free AI Logger WordPress plugin automatically tracks LLM bot crawls on your site and can generate and manage your `llms.txt` file, a crucial optimization task. This makes it uniquely designed for WordPress websites.
What truly sets Cairrot apart for agencies is the combination of its most affordable pricing model (pay-per-client, cancel anytime) and its commitment to accessibility. It’s the only tool that offers Grok tracking as an add-on for any plan, and the only tool that will track 5 major LLM platforms for under $100. For agencies looking to offer cutting-edge GEO services without destroying their margins, Cairrot is the clear winner.
2. Profound (Best for Ecommerce Visibility)

Profound positions itself as an enterprise-grade platform, and it has the feature set and price tag to match. It’s particularly strong for large e-commerce brands due to its specialized shopping optimizations for ChatGPT.
- Key Features: Real-time monitoring, agent analytics for crawler visibility, content optimization workflows, SOC 2 Type II compliance.
- Pricing: Starts at $99/month, but that’s for ChatGPT only. Expect costs to rise significantly as you add more models and features.
- Free Trial: No, but a demo is available.
- API: No public API is advertised, suggesting it’s likely reserved for custom enterprise deals.
- Integrations: Custom content workflow integrations.
While powerful, its claim of providing “AI search volumes” is something I’m critical of (no LLM offers this data publicly, yet). For a large e-commerce company that needs SOC 2 compliance and has a dedicated GEO budget, Profound is a strong contender. However, its pricing model and lack of a flexible API make it a tough sell for most agencies.
3. Gumshoe AI (Best Pay-Per-Report Visibility Tool)

Gumshoe AI takes a completely different approach. Instead of a monthly subscription, you pay per report. This is perfect for one-off projects, initial client audits, or teams that don’t need continuous monitoring.
- Key Features: Persona-specific visibility analysis, tactical recommendations, competitive ranking comparisons, source citation tracking.
- Pricing: Starts as low as $30 per report.
- Free Trial: Yes, your first few reports are free.
- API: Yes, but it’s on their Enterprise plan.
- Integrations: Custom integrations are available for enterprise clients.
The beauty of Gumshoe is its simplicity. You define your brand, competitors, and prompts, and you get a detailed report. It’s an excellent way to dip your toes into GEO without committing to a monthly fee. The downside is that costs can add up quickly if you need frequent monitoring, and it lacks the continuous, dashboard-style view of a SaaS platform.
4. AthenaHQ (Premium GEO Tool for High Tech Companies)
AthenaHQ comes with an impressive pedigree, backed by experts from Google, DeepMind, and OpenAI. It’s a premium tool focused on sophisticated strategies like “competitor impersonation” and “blindspot detection.”
- Key Features: Two-dimensional GEO optimization, dynamic AI crawling, Athena Citation Engine (ACE), self-improving content AI agents.
- Pricing: Starts at $295/month.
- Free Trial: No, but a first-month discount is offered.
- API: No.
- Integrations: No public integrations listed.
AthenaHQ is for teams that want to be on the absolute bleeding edge and have the budget for it. The lack of an API and public integrations makes it a bit of a walled garden, which can be a challenge for agencies needing to integrate data. It’s a powerful but expensive tool for those who want AI to not just track, but also strategize.
5. Evertune (Best Enterprise GEO Tool for Fortune 500 Size Companies)
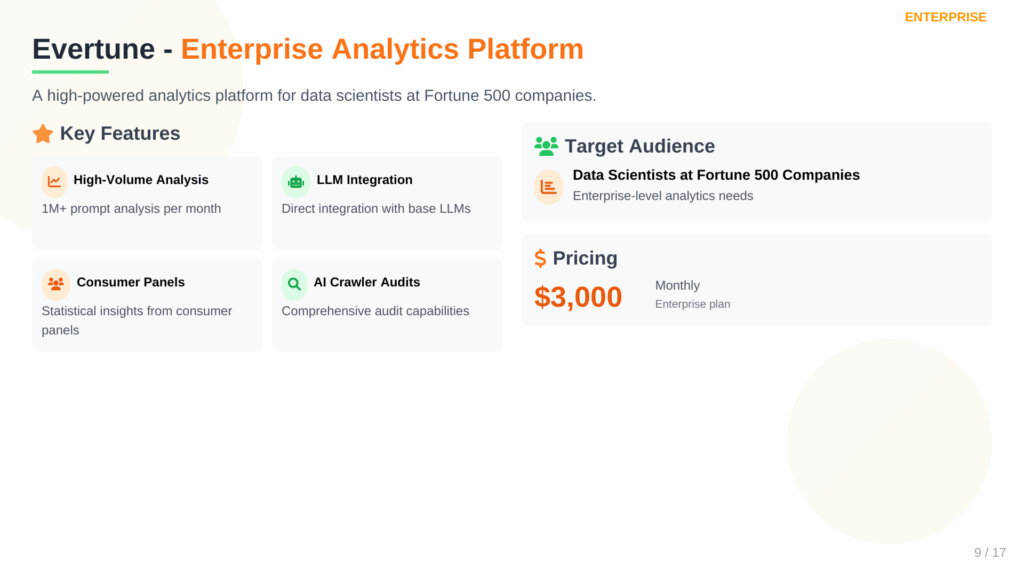
If you’re a data scientist at a Fortune 500 company tasked with understanding AI visibility, Evertune is built for you. With a starting price of $3,000/month, it’s in a different league entirely.
- Key Features: High-volume prompt analysis (1M+ per month), direct integration with base LLMs, consumer panels for statistical insights, AI crawler audits.
- Pricing: Starts at $3,000/month.
- Free Trial: No.
- API: No, it seems to be a closed platform.
- Integrations: Partnership with impact.com for affiliate actions.
Evertune isn’t a tool for a typical marketing agency. It’s a high-powered analytics and business intelligence platform for enterprises where AI is a primary marketing and research channel. The cost is prohibitive for almost everyone else, but for its target market, the depth of data is unparalleled.
6. Scrunch AI (Premium AI Monitoring and Optimization Tool for Agencies)
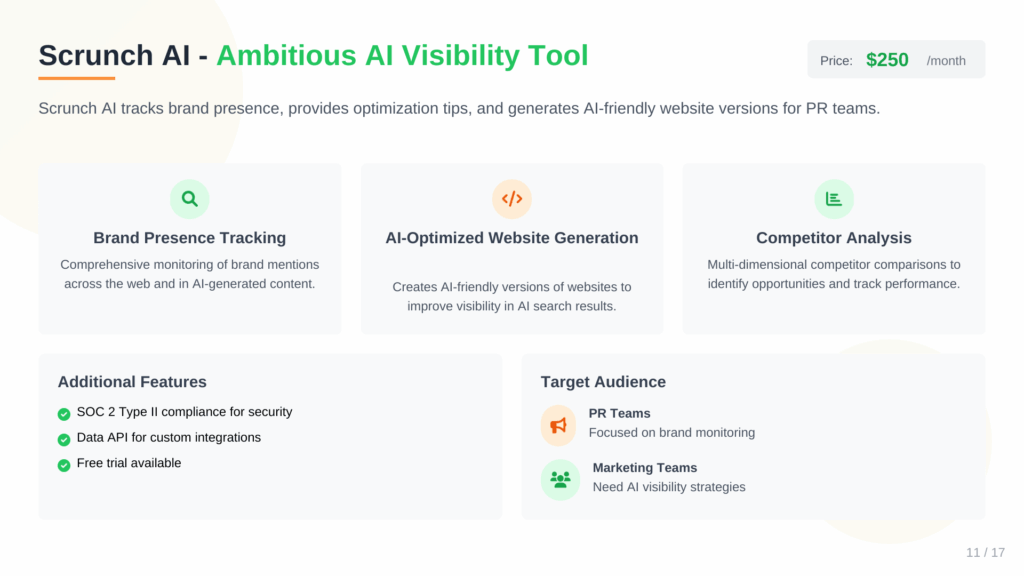
Scrunch AI is an ambitious platform that tries to do it all: track brand presence, provide optimization tips, and even generate AI-friendly versions of your website through its “Agent Experience Platform.”
- Key Features: AI bot crawling, AI-optimized site versions, multi-dimensional competitor comparisons, SOC 2 Type II compliance.
- Pricing: Starts at $250/month.
- Free Trial: Yes.
- API: Yes.
- Integrations: Data API for custom integrations.
Like Profound, Scrunch AI is SOC 2 compliant, making it a good fit for enterprise clients. However, its pricing model is fixed, which is a drawback for agencies. While the idea of an “Agent Experience Platform” is intriguing, I often find that tools trying to be both the analytics platform and the implementation solution can be a master of none.
7. Semrush AI Visibility Toolkit (Best for Marketing Agencies Not Specialized in SEO)
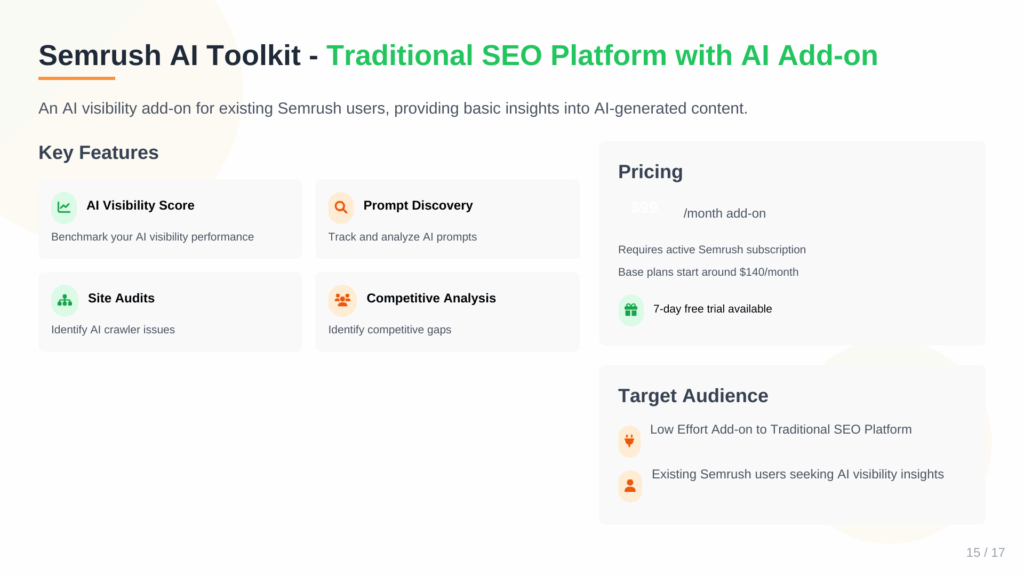
Semrush’s AI Visibility Toolkit is an add-on designed as an extension of their established SEO platform, allowing users to dip into GEO without switching tools. It’s a convenient choice for teams already invested in Semrush, providing basic insights into AI-generated answers. However, it lacks the depth and precision of dedicated LLM trackers, making it feel more like a bolt-on feature than a standalone solution.
- Key Features: AI Visibility Score for benchmarking, sentiment and perception analysis, prompt discovery and tracking, site audits for AI crawler issues, competitive gap identification, report generation.
- Pricing: Starts at $99/month as an add-on. Requires an active Semrush subscription (base plans start around $140/month), so total costs can exceed $200/month quickly.
- Free Trial: Yes (7 days).
- API: No.
- Integrations: Integrates with Semrush’s core SEO tools, including keyword research, backlink analysis, and reporting dashboards.
For SEO teams already using Semrush, this toolkit is a low-effort way to start monitoring AI visibility without adding a new vendor. The unified dashboard is a plus, combining traditional SEO metrics with AI data. That said, its reliance on probabilistic modeling rather than direct LLM access can lead to less accurate insights, and the add-on pricing feels steep for what it offers compared to dedicated tools. If you’re not locked into Semrush, more specialized options like Cairrot, and Gumshoe AI, and even AthenaHQ provide better value and flexibility for pure GEO needs.
Find Detailed Comparisons of GEO Tools
Among the seven software tools mentioned so far, there is a strong option for pretty much every type of marketer (or marketing agency) that wants to break into AI visibility tracking. But we go into greater detail for each competitor (and review 4 others) in our comparison of the 11 Best LLM Tracking Tools ->
But a complete GEO software stack doesn’t stop at tracking; it includes categories like AI SEO Content/Content Optimization (Jasper, Surfer SEO) and Technical SEO (Wordlift, Search Atlas), among others. Check out WordPress Dynamic’s AI SEO Tool Guide (33 GEO Tools Compared) for a zoomed out perspective ->
Are GEO and AEO Actually Different?

As the field of AI search optimization has emerged, so have new acronyms. The two most popular are AEO (Answer Engine Optimization) and GEO (Generative Engine Optimization).
Some SEO experts and industry analysts argue for a technical distinction between the two terms. In this view:
- AEO should refer to optimizing for answer-focused features within traditional search engines, such as Google’s AI Overviews, featured snippets, and knowledge panels.
- GEO should refer specifically to optimizing for visibility within standalone conversational LLM tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude.
However, many other marketing leaders and practitioners argue that this distinction is largely academic. The vast majority of people use the terms interchangeably to describe the overall practice of optimizing for AI-generated answers, regardless of the platform. The underlying strategies for both often overlap significantly, focusing on structured content, authority, and clarity.
Do We Treat GEO and AEO the Same? Yes.
At Cairrot, our team uses GEO and AEO interchangeably. We recognize that while a technical difference can be argued, in practice, they refer to the same strategic goal: ensuring your brand is visible and trusted in the age of AI search. We believe that forcing a rigid distinction creates unnecessary confusion for marketing teams who are simply trying to adapt to this new landscape.
Will GEO or AEO Become the More Popular Term?
While GEO is currently very popular, we believe AEO will win in the long term.
We debated this internally, and even though some of personally prefer to say “GEO,” we all agreed that most SEO experts will eventually get annoyed when they try to optimize for GEO.
The acronym “GEO” is already commonly used in other contexts (e.g., geography, geology, geostationary orbit), which could create SEO challenges and ambiguity for tools, agencies, and experts trying to rank for the term. Because “AEO” is more unique and directly describes the goal (optimizing for AI-generated answers regardless of which platform they are served in, not just generative tools like LLMs), we predict it will become the standard acronym in the years to follow, even if GEO remains more popular through 2026.
Tips for Learning GEO Quickly
The field of GEO is evolving at a breakneck pace, but you can get up to speed quickly by focusing on a combination of foundational knowledge, practical application, and following the right experts. Here are some tips to accelerate your learning:
- Follow Key Experts: The GEO community is highly active on platforms like LinkedIn and X. Following leading practitioners will give you access to real-time insights, case studies, and emerging tactics. See our recommended list below.
- Add AI Traffic as a Channel in GA4: You can’t improve what you don’t measure. If your website already receives over 1,000 clicks per month from organic search, you probably receive enough referral traffic from LLMs that it is worth checking. Anybody can do this in a few minutes, just follow the steps laid out here: How to track your AI Search Traffic (referral traffic from LLMs) for free ->
- Conduct Manual Audits: The best way to learn is by doing. Take your top 10 business-critical queries and manually test them in ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity. Analyze the results: Who is being cited? What sources are used? What is the structure of the content that wins? Document your findings in a spreadsheet.
- Experiment with Different Tools: And not just free trials of AI visibility tools like Cairrot. You should experiment with content generation tools, Use them to run an audit on your own site. Seeing real data on your AI visibility (or lack thereof) is a powerful motivator and learning tool.
11 Respected Industry Experts to Follow When Learning GEO
| GEO Expert | What They Share | Most Active Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Mike King (iPullRank) | Deeply technical and strategic playbooks on "relevance engineering" for AI Mode and GEO. Mike launched the SEO Week conference in 2025, widely cited by many SEO experts (including myself) as the best American conference for new AEO/GEO tactics. | LinkedIn / Blog |
| Jori Ford | Focuses on "Hybrid Engine Optimization," blending product, marketing, and SEO for visibility in "agent-led discovery." Jori taught Connor Kimball how to track crawls from LLM agents at SEO Week in 2025, which eventually became the inspiration for Cairrot’s AI Logger plugin. | |
| Cyrus Shepard (Zyppy) | Publishes research and experiments on how AI Overviews shift clicks and impact visibility. Cyrus regularly shares his insights on X and his website, and he is a regular on SEO industry podcasts. | X / Blog |
| Lily Ray (Amsive) | Provides deep, ongoing analysis of the impact of AI Overviews and shares practical experiments. Lily also has some of the more humorous commentary on the evolution of Google’s AI Overviews and AI Mode. | X / LinkedIn |
| Aleyda Solís | Creates actionable "AI Search" checklists and visuals that bridge classic SEO with AEO/GEO. Aleyda is a known workhorse in the SEO industry, always bringing actionable checklists to speaking events and podcast appearances. | |
| Connor Kimball (Cairrot) | Actively shares results from GEO campaigns and experiments for websites in several niches, including global SaaS, B2B industrials, law firms, financial services, cosmetic clinics, and ecommerce stores. As part of his role at Cairrot, Connor frequently shares observations about LLM ranking behavior based on the most up-to-date data in virtually every online niche. | YouTube / LinkedIn |
| Matthew Bertram (EWR Digital) | As the Head of Marketing at EWR Digital, a premier AI SEO agency serving B2B energy companies, and the host of The Best SEO Podcast, Matthew (Matt) regularly shares field observations and interviews the top names in AI on his podcast. | LinkedIn / Podcast |
| Kyle Roof (Page Optimizer Pro) | Uses scientific on-page SEO testing and data to create blueprints for ranking in generative answers. | YouTube / Website |
| Clint Butler (Digitaleer) | Expert in structured data, schema optimization, and entity-based visibility for AI search. | LinkedIn / YouTube |
| Ted Kubaitis (seotoollab.com) | Provides data-driven analysis of SEO ranking factors and their correlation with AI visibility. | LinkedIn / YouTube |
| Jono Alderson | Focuses on the intersection of WordPress, structured data, and building for an AI-mediated web. | Blog / LinkedIn |
At Cairrot, our team uses AEO and GEO interchangeably. We recognize that while a technical difference can be argued, in practice, they refer to the same strategic goal: ensuring your brand is visible and trusted in the age of AI search. We believe that forcing a rigid distinction creates unnecessary confusion for marketing teams who are simply trying to adapt to this new landscape.
Run a GEO Audit On Your Website for Free
Navigating the world of GEO can be complex, but choosing the right tool doesn’t have to be. If you’re a marketing agency or a business running on WordPress, we built Cairrot for you.
You can sign up for a free trial to explore the full platform. After that, it’s only $39 to experience a full month of powerful LLM analytics and GEO insights.

